Osteochondrosis means a pathology of the spine, the morphological substrate (base) of which is a violation of the structure of the intervertebral discs.However, this concept is not entirely correct, since according to Western medical terminology, this nosological form means degeneration of ossification centers, which is possible only in childhood.At the same time, the relevance of the issue in this case does not depend on the name, even if domestic doctors have a traditional opinion about the disease.In this article we will talk about the treatment of osteochondrosis at home, as well as the prevention and diagnosis of this disease.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis
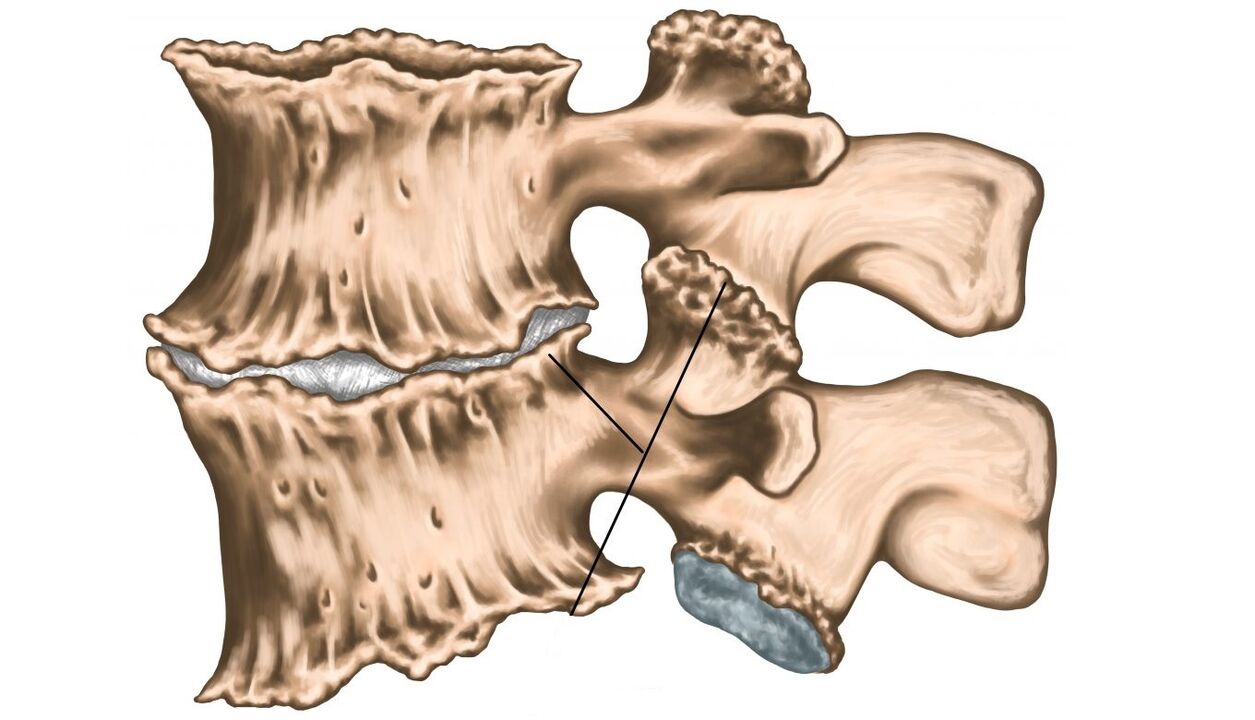
With osteochondrosis, the intervertebral foramina narrow, as a result of which blood vessels and nerves are pinched, and bone tissue growths (osteophytes) appear on the edges of the vertebrae.
The morphology of the disease is quite specific.The pathology is an age-related change in the intervertebral discs, which lose their elastic properties and become compressed with increasing age.
This causes the vertebrae to move a little closer together and the intervertebral foramina, through which the spinal nerves exit, narrows, deforms and interrupts conductivity.For this reason, not entirely typical symptoms are noted, which consist in the manifestation of local pain in the muscles and limbs.
Symptomatically it resembles radiculitis, spina bifida, tumor formations of the skeletal system of the spine and the membranes of the spinal cord.Therefore, a visit to the doctor is necessary both to make a diagnosis of osteochondrosis and to exclude these serious pathologies.
If symptoms such as weakness in a limb occur, it is advisable to consult a doctor immediately.If long-term operations related to arm movement are not possible, osteochondrosis is localized in the neck area, and if such symptoms are noted in the lower extremities, the lumbar spine is affected.
Differentiating the complaints of patients with osteochondrosis of the thoracic spine is relatively difficult, since autonomic disorders associated with cardialgia, impaired external breathing and symptoms of shortness of breath are most often observed there.
The disease is diagnosed based on anamnesis.This must contain information about the workplace and working hours.Here it is of some importance to establish the fact of lifting weights.Diagnosis using laboratory methods is not possible, since the process is essentially natural and manifests itself with age.It is also non-inflammatory in nature.Instrumental methods include X-ray of the spine in a specific section.This allows us to determine the degree of narrowing of the lumen between the bodies of two adjacent vertebrae and, accordingly, confirm the morphological substrate of the pathology.Methods such as CT and MRI can confirm the diagnosis in more detail and exclude similar nosological forms.
Treatment of osteochondrosis and prevention
Preventive measures to prevent osteochondrosis include physical exercises related to gymnastics, running and pull-ups.At the same time, heavy lifting leads to an aggravation of the disease.Often it can appear for the first time precisely during this manipulation.When lifting a load, the patient feels tingling, numbness in the extremity and in the shoulder blade area.
Treatment of osteochondrosis is conservative in nature and is aimed at reducing the manifestations of symptoms, since it is almost impossible to eliminate the root cause.To alleviate the symptoms, irritants are used that reflexively increase conductivity in the nerve trunks.For the treatment of osteochondrosis at home, ointments with menthol, pepper plasters and mustard plasters can be recommended.A heating pad can be applied locally.At the same time, physiotherapeutic methods can alleviate the corresponding symptoms.In particular, you can undergo electric shock sessions in the clinic.
Pharmacological treatment includes analgesic therapy and agents to improve nerve conduction.The first group of drugs includes non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.These are drugs that are administered intramuscularly or orally.The dosage regimen is determined by the doctor.As a drug of the second group, a drug is effective that partially reduces the deficiency of nerve trophism.At the same time, care is not required for patients, since performing everyday manipulations does not cause them any particular difficulties, with the exception of physical work, which they are not recommended to perform.
Which doctor should I contact?
The manifestations of spinal osteochondrosis are caused mainly by compression of the roots of the spinal cord, which emerge through the narrowed openings between the vertebral processes.Therefore, this disease is traditionally treated by a neurologist.In addition, it is advisable to consult a vertebral doctor - a specialist in spinal diseases - or an orthopedist.A physiotherapist, a specialist in physiotherapy and massage, a chiropractor, an osteopath and a reflexologist will support you in the treatment.




















